Minikube is local Kubernetes, focusing on making it easy to learn and develop for Kubernetes.
All you need is Docker (or similarly compatible) container or a Virtual Machine environment, and Kubernetes is a single command away: minikube start
Prerequisites:
2 CPUs or more
2GB of free memory
20GB of free disk space
Internet connection
Container or virtual machine manager, such as: Docker, QEMU, Hyperkit, Hyper-V, KVM, Parallels, Podman, VirtualBox, or VMware Fusion/Workstation
A server running on one of the following operating systems: Ubuntu 22.04, 20.04, 18.04, 16.04 or any other Debian-based distribution like Linux, CentOS, or Fedora.
Access to the root user
Now, let’s get started with the installation.
Installation Step:
In this article, we will be using Docker container as a base for Minikube.
- To install Docker on Linux :
Update the installed packages and package cache on your instance.
sudo yum update -y
- Install the most recent Docker Community Edition package:
sudo yum install -y docker
- Updating system packages and installing Minikube dependencies:
sudo yum update -y
sudo yum install -y curl wget apt-transport-https
- Start the Docker service:
sudo service docker start
- Add the
meghauser to thedockergroup so that you can run Docker commands without using sudo.
sudo usermod -a -G docker megha
- Verify that the
meghauser can run Docker commands without using sudo.
docker ps
You should see the following output, confirming that Docker is installed and running:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
Installing Minikube:

To install the latest minikube stable release on x86–64 Linux using binary download in Linux Operating System:
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64
Once the binary is downloaded, copy it to the path /usr/local/bin and set the executable permissions on it:
sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube && rm minikube-linux-amd64
Debian package:
To install the latest minikube stable release on x86–64 Linux using Debian package:
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube_latest_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i minikube_latest_amd64.deb
RPM package:
To install the latest minikube stable release on x86–64 Linux using RPM package:
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-latest.x86_64.rpm
sudo rpm -Uvh minikube-latest.x86_64.rpm
Verify the minikube version:
minikube version
#output
minikube version: v1.32.0
commit: 8220a6eb95f0a4d75f7f2d7b14cef975f050512d
Note: At the time of writing this tutorial, the latest version of minikube was v1.32.0
Install and Set Up kubectl on Linux:

kubectl is the command-line interface (CLI) tool used to interact with Kubernetes, an open-source platform for managing containerized applications and services. It allows you to control and manage Kubernetes clusters by performing various operations, such as deploying applications, scaling workloads, managing resources, and troubleshooting.
Install kubectl binary with curl on Linux:
Download the latest release with the command:
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
Note: To download a specific version, replace the $(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt) portion of the command with the specific version.
For example, to download version 1.31.0 on Linux x86–64, type:
curl -LO https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.31.0/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
And for Linux ARM64, type:
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/arm64/kubectl"
Once Kubectl is downloaded, set the executable permissions on the Kubectl binary and move it to the path /usr/local/bin.
chmod +x kubectl
mv ./kubectl ~/usr/local/bin/
Now verify the kubectl version:
kubectl version -o yaml

Or use this for detailed view of version:
kubectl version --client --output=yaml
Start minikube:
minikube start
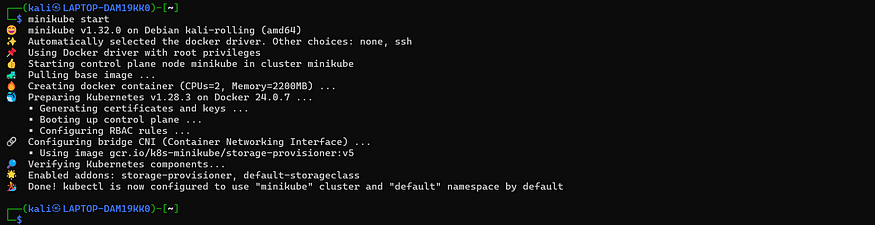
The above picture confirms that the Minikube cluster has been started successfully.
Verifying Installation:
Run the below minikube command to check the status.
minikube status

Run the following kubectl command to verify the Kubernetes version, node status, and cluster info.
kubectl cluster-info
Kubernetes control plane is running at https://192.168.1.0:8443
CoreDNS is running at https://192.168.1.0:8443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
kubectl get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
minikube Ready control-plane 10m v1.28.3
Managing Addons on minikube:
By default, only a couple of addons are enabled during minikube installation. To see the addons in Minikube, run the below command.
minikube addons list

If you wish to enable any addons, run the below minikube command.
minikube addons enable metrics-server
Let’s access the Kubernetes dashboard.
Run this commands:
minikube dashboard

Paste the URL on browser and See the Kubernetes Dashboard:

